[ad_1]
Tuberculosis (TB) is as soon as once more the infectious illness chargeable for the most deaths worldwide, according to a Tuesday announcement from the World Health Organization (WHO).
The contagious illness was chargeable for 1.25 million world deaths in 2023, WHO reported, together with 161,000 folks with HIV.
COVID-19 had overtaken TB as the world’s main infectious killer for the earlier three years.
LASSA FEVER DEATH REPORTED IN MIDWESTERN STATE, CONTACT TRACING BEGINS
What to learn about tuberculosis
TB is a preventable and curable illness attributable to micro organism that usually impacts the lungs, according to WHO.
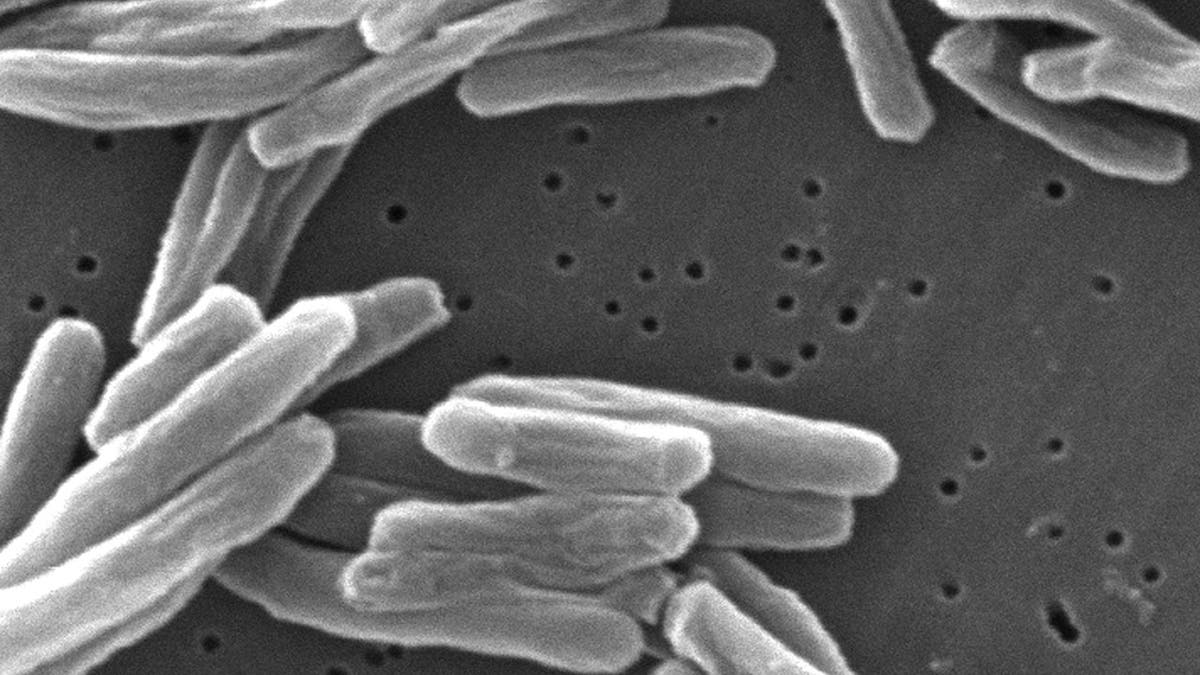
This 2006 electron microscope picture offered by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reveals Mycobacterium tuberculosis micro organism, which causes the illness tuberculosis. (Janice Carr/CDC/AP)
It is an airborne contagion that may be unfold via coughing, sneezing or saliva.
While round 25% of individuals have seemingly been contaminated with the micro organism, solely 5% to 10% will expertise signs and develop the illness, the similar supply acknowledged.
Only folks with signs can unfold the illness.
Who is in danger?
“If you breathe, you can catch TB — so all people are at risk,” Masae Kawamura, M.D., a former TB management director in San Francisco and a tuberculosis clinician, advised Fox News Digital.
Kawamura calls TB a “social disease of crowding and mobility.”
E. COLI OUTBREAK LINKED TO MCDONALD’S BURGERS: HOW TO SPOT THE SYMPTOMS
“Since TB is airborne, congregate settings like hospitals, nursing homes, prisons, jails, classrooms and homeless shelters are places TB is more easily spread, especially if multiple risks are involved,” she stated.
Those at the highest threat of growing TB illness after publicity embrace individuals who have diabetes, have weakened immunity, are malnourished, use tobacco and/or drink extra quantities of alcohol.
Babies and kids are additionally at greater threat.
“If a person has latent TB infection, TB disease activation varies from 5% to 15% over a lifetime, but can be higher if a person has multiple risks, such being an elderly person and/or being malnourished, having diabetes and/or having other diseases that weaken the immune system,” stated Kawamura.
Symptoms, analysis and therapy
Those who get sick with TB could expertise gentle signs, together with coughing, chest ache, fatigue, weight reduction, weak point, fever and evening sweats, according to WHO.
Symptoms will fluctuate relying on which organs are affected.
“If you breathe, you can catch TB — so all people are at risk.”
In addition to the lungs, the illness may also have an effect on the kidneys, backbone, pores and skin and mind.
“TB can affect any organ of the body, but it causes disease in the lung in over 80% of cases,” stated Kawamura.
“This is dangerous because it causes cough, the mechanism of airborne spread.”

TB is an airborne contagion that may be unfold via coughing, sneezing or saliva. (iStock)
In extra extreme circumstances, sufferers could cough up blood, famous Kawamura, who serves on the board of administrators of Vital Strategies, a world public well being group.
“Often there are minimal signs for a very long time and folks mistake their occasional cough with allergic reactions, smoking or a chilly they can not shake off,” she added.
CLICK HERE TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP
TB will be recognized with speedy diagnostic checks, WHO famous.
The illness is handled with antibiotics which might be taken day by day for 4 to six months, the similar supply acknowledged. Some of the commonest embrace isoniazid, rifampicin, pyrazinamide and ethambutol.
“TB can affect any organ of the body, but it causes disease in the lung in over 80% of cases,” an knowledgeable stated. “This is dangerous because it causes cough, the mechanism of airborne spread.” (iStock)
Failing to take the full course of medicines may cause the micro organism to turn out to be drug-resistant.
Cases of drug-resistant TB want to be handled with completely different drugs.
When TB turns into lethal
If TB goes untreated, it is deadly in about half of its victims, according to Kawamura.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
“About 25% recover on their own and another 25% persist as chronic active TB cases,” she stated.
In the U.S., most lively TB circumstances are detected at an earlier stage, the knowledgeable famous, however the loss of life fee is nonetheless “shockingly high” at 10%, and far greater if the affected person is over 65 years outdated.
Prevention of the illness
There is a childhood vaccine referred to as BCG (Bacille-Calmette-Guerin) that is given in most of the world to infants, Kawamura famous.
“It reduces death, meningitis and organ dissemination by 75% in children under 5 — however, it does not prevent TB infection and is ineffective in adults,” the physician advised Fox News Digital.

The finest technique of prevention is testing these in danger and treating latent tuberculosis an infection (LTBI), a health care provider suggested. (iStock)
“Overall, BCG is considered ineffective, hence, TB’s title as the greatest infectious disease killer of all time.”
BCG was by no means utilized in the U.S. due to the nation’s decrease charges of TB, its ineffectiveness and its interference with TB checks, she added.
For extra Health articles, go to www.foxnews.com/well being
The finest technique of prevention is testing these in danger and treating latent tuberculosis an infection (LTBI), according to the physician.
[ad_2]
Source hyperlink





