[ad_1]
Your help helps us to inform the story
This election remains to be a lifeless warmth, based on most polls. In a struggle with such wafer-thin margins, we’d like reporters on the bottom speaking to the folks Trump and Harris are courting. Your help permits us to maintain sending journalists to the story.
The Independent is trusted by 27 million Americans from throughout your complete political spectrum each month. Unlike many different high quality information retailers, we select to not lock you out of our reporting and evaluation with paywalls. But high quality journalism should nonetheless be paid for.
Help us preserve deliver these crucial tales to mild. Your help makes all of the distinction.
A brand new examine claims that weekend bouts of exercise could also be simply nearly as good for you as figuring out in the course of the week.
The examine examined two units of survey information from the Mexico City Prospective Study, and discovered that the danger of “mild dementia” was lowered by a median of 15% within the “weekend warriors” – who exercised a few times per week – and by 10% within the “regularly active” – who exercised extra typically.
However, after taking account of things which may affect the outcomes, akin to age, smoking, sleep period, eating regimen and alcohol consumption, the researchers steered each exercise patterns had related results.
How does exercise impact our brains?
Regular exercise has a variety of advantages for our reminiscence and cognitive skills.
“Immediately after exercise there’s an increase in oxygenated blood, and glucose is mobilised,” explains Rachael Mackenzie, neurological physiotherapist and director at Workathlete. “The neurotransmitters that are released after exercise are also directly active in the regions of the brain responsible for memory and learning.”
Physical exercise might additionally affect the quantity of our hippocampus – a small construction which helps us with reminiscence and achieve consciousness from our surroundings.
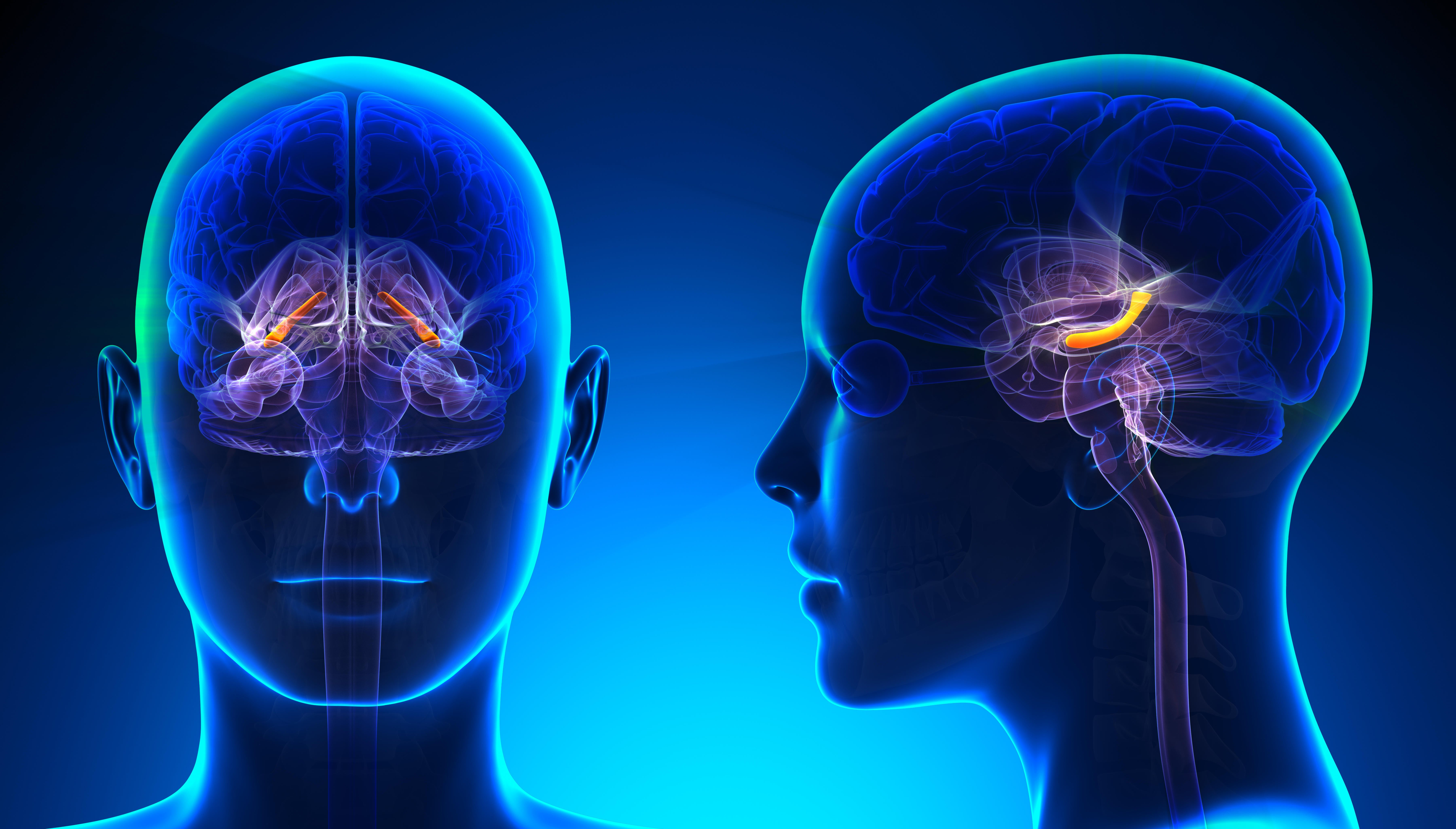
“Over time, we see that children and adults who exercise have more volume in the hippocampus and an increased connection across the regions of the brain involved in thinking, planning and problem solving,” says Mackenzie.
Exercise additionally stimulates the manufacturing of brain-derived-neurotrophic issue, which Mackenzie describes as a “miracle grow for the brain”.
“This growth factor helps to maintain brain cells, stimulate connection between brain cells and helps the brain maintain plasticity,” explains Mackenzie. “Effectively, it creates new connections, allowing new learning to happen across the lifespan.”
Meanwhile, regular exercise might additionally assist forestall or delay the onset of dementia.
“People who exercise are less likely to develop dementia,” says Mackenzie. “This is partly because of the reduced risk of developing the metabolic risk factors for dementia (like diabetes or cardiovascular disease) but also because of the way exercise protects brain cells and the connection between brain cells through the activity of brain-derived-neurotrophic factor and other neurotrophic factors.”
Can exercise assist enhance our psychological well being?
“Exercise has a direct effect on reducing rates of depression across the population,” highlights Mackenzie. “Exercise reduces the amount of stress hormones circulating and increases the amount of dopamine – the happy hormone – in the brain.”

Aerobic exercise specifically might assist folks cope higher with stress.
“Aerobic exercise that involves a switch between high-intensity and moderate to low-intensity helps to train the stress response system to move between fight and flight mode (sympathetic activity) and rest/recovery mode (parasympathetic activity),” explains Mackenzie. “This helps to train the stress response system to recover. So, when stressful events happen during the day, a person doesn’t stay in stress mode and their nervous system is conditioned to recover.”
What varieties of exercise is especially stimulating for the brain?
If you might be on the lookout for an exercise to stimulate your brain and physique then look no additional as Jade Imani, certified private coach with Insure4Sport, has compiled an inventory of suggestions for the next age teams…
Ages 20-30
High-intensity interval coaching (HIIT)

“HIIT workouts boost cardiovascular health, which is beneficial for memory and mental clarity,” explains Imani. “HIIT’s varying intensity also keeps the brain engaged.”
Team sports activities
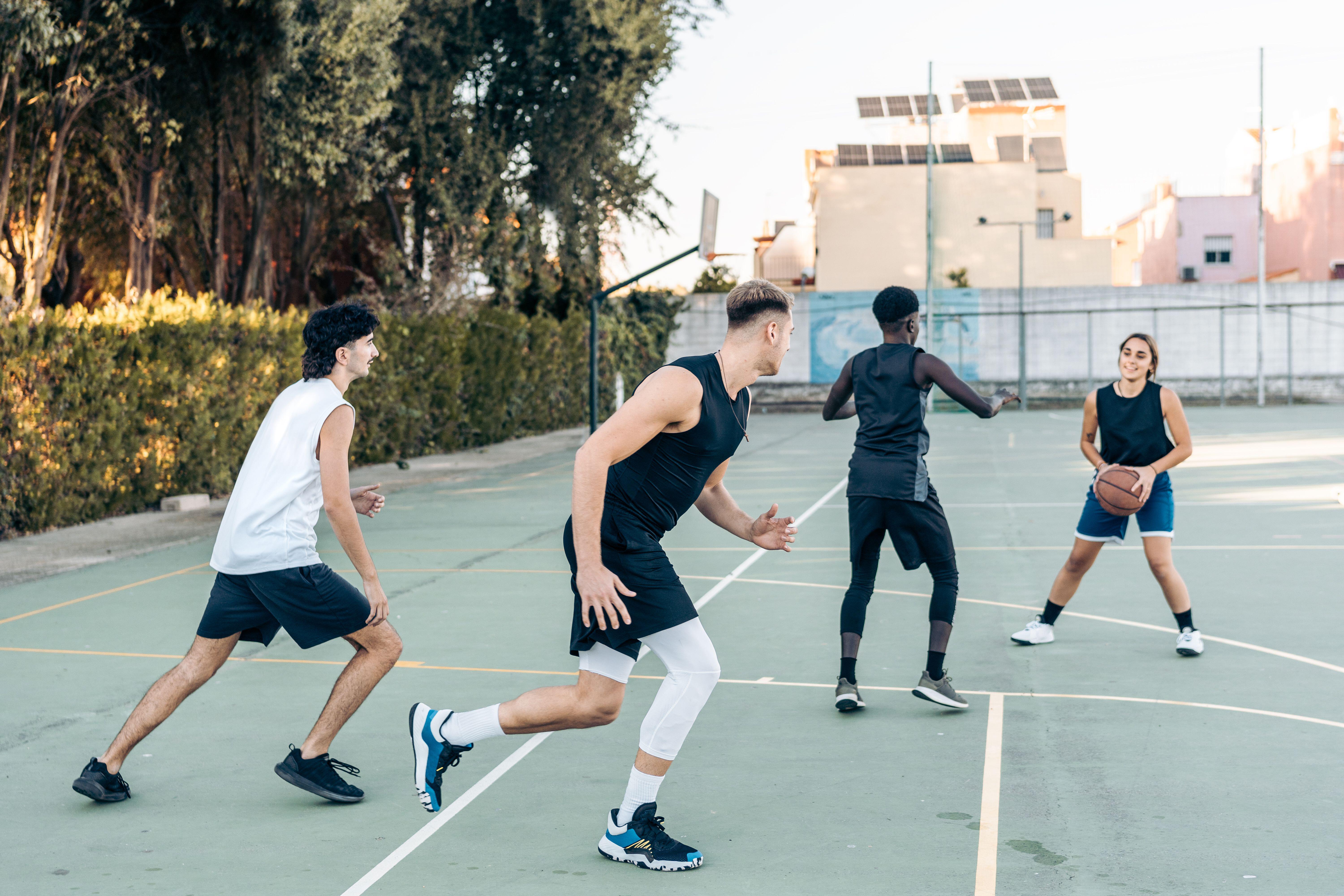

“Basketball, soccer, and similar sports require strategy, quick thinking, and social interaction, all beneficial for cognitive health,” highlights Imani.
Mackenzie provides: “Team and racket-based sports involve short bursts of high-intensity exercise such as chasing the ball, followed by periods of lower intensity.
“And the bonus is that they are done with other people, in a community – so we add in the positive effect of social connection, which reduces the risk of developing mental health conditions and dementia.”
Ages 30-40
Running or brisk strolling
“Long, moderate-intensity runs or brisk walks help maintain cardiovascular health, supporting brain function,” explains Imani.
Yoga and pilates
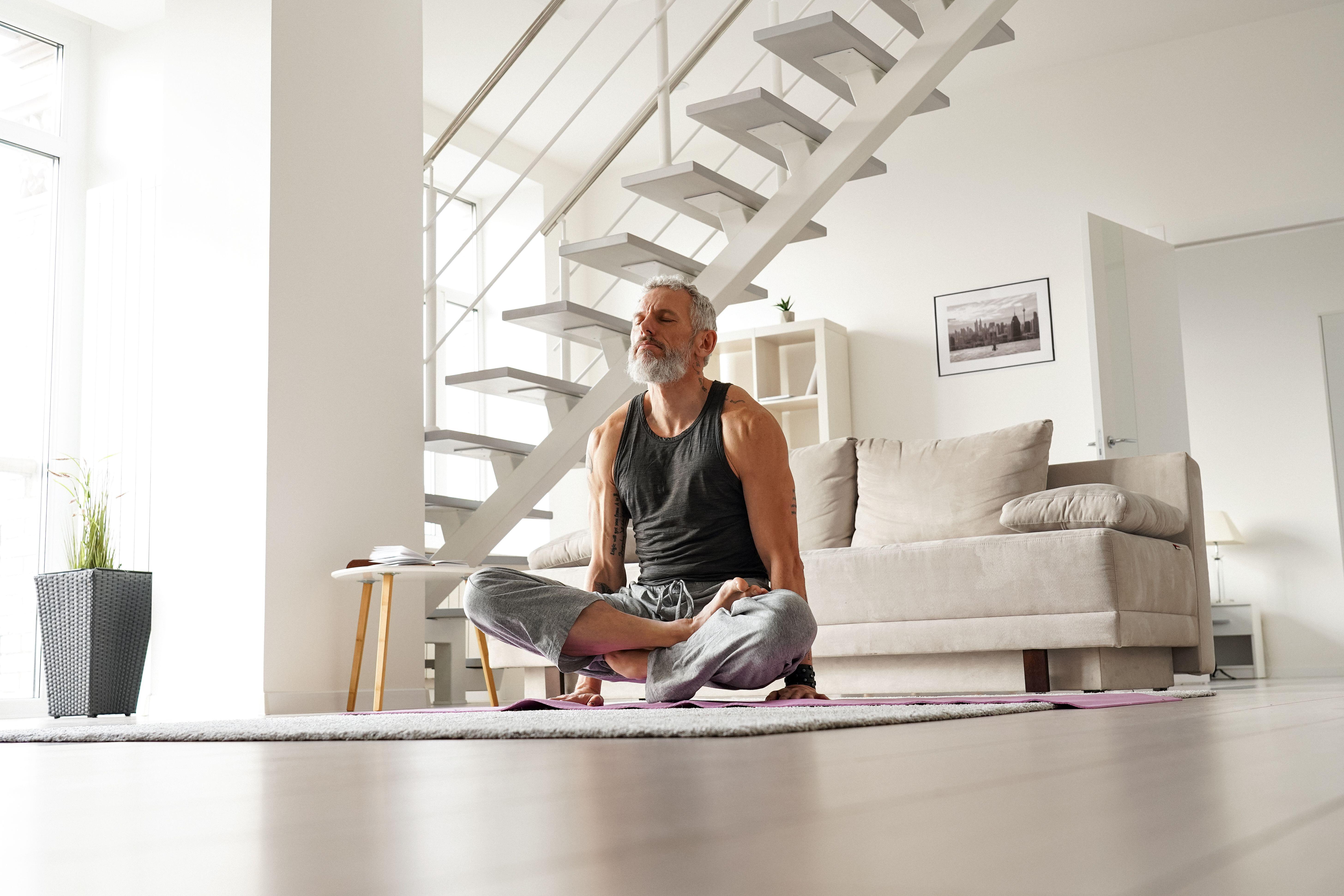

“These activities build mind-body awareness and reduce stress, which can protect against cognitive decline,” notes Imani. “More challenging postures also improve focus.”
Ages 50-60
Strength coaching
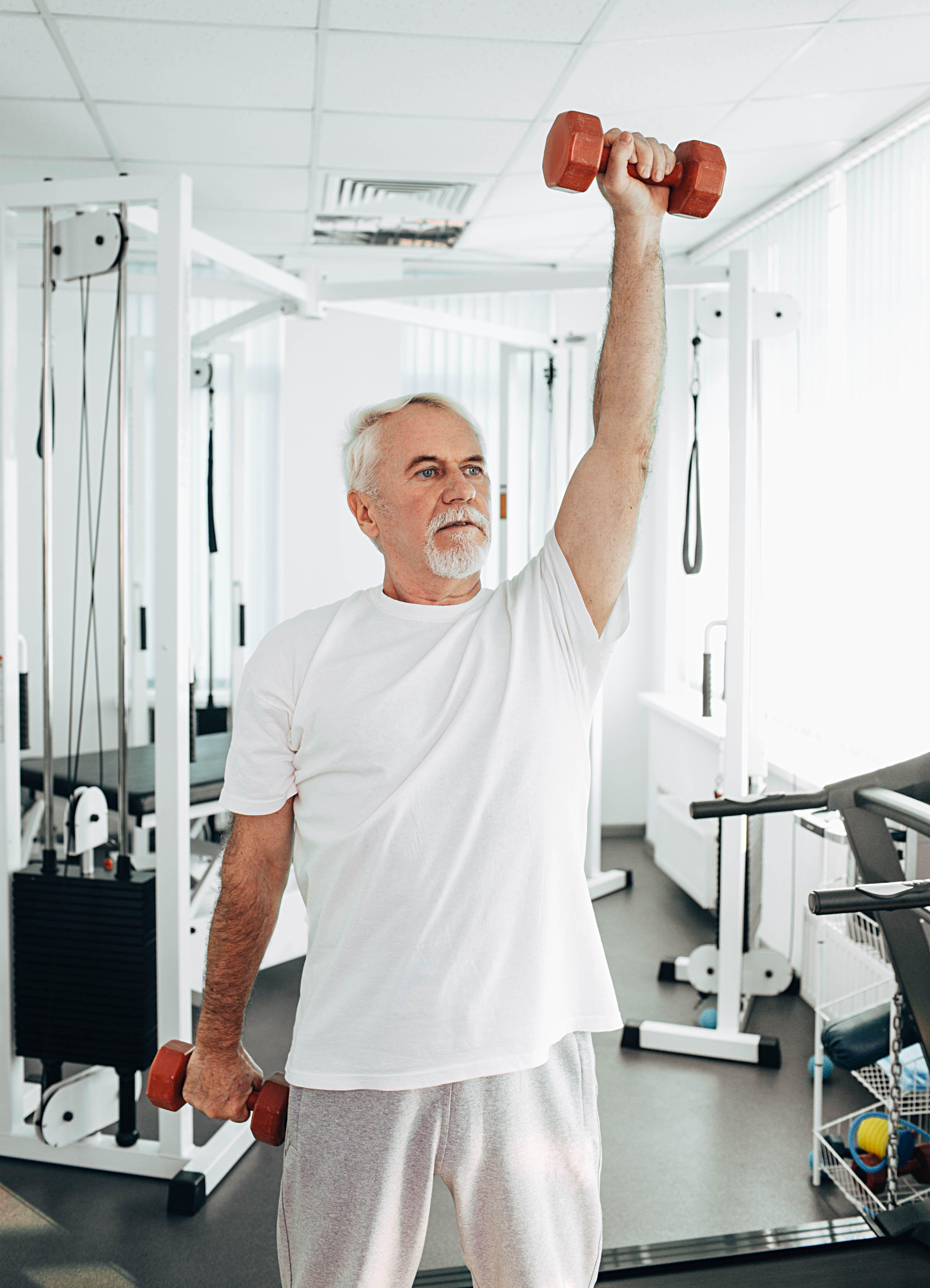

“Regular weightlifting supports cognitive health by increasing blood flow to the brain and supporting brain-derived neurotrophic factor, crucial for neuroplasticity,” states Imani.
Tai Chi
“This practice involves slow, controlled movements, which improve balance and focus, helping with memory and attention,” says Imani.
[ad_2]
Source hyperlink





