[ad_1]
- Earth’s changing spin is inflicting it to rotate barely sooner than earlier than, which may result in the subtraction a second from clocks round 2029.
- This phenomenon, whereas not catastrophic, is unprecedented, in keeping with geophysicists.
- Melting ice on the poles has countered Earth’s elevated pace, delaying the necessity for a detrimental “leap second” by about three years.
Earth’s changing spin is threatening to toy with our sense of time, clocks and computerized society in an unprecedented approach — however just for a second.
For the primary time in historical past, world timekeepers may have to think about subtracting a second from our clocks in a few years as a result of the planet is rotating a tad sooner than it used to. Clocks may should skip a second — known as a “negative leap second” — round 2029, a research within the journal Nature stated Wednesday.
“This is an unprecedented situation and a big deal,” stated research lead creator Duncan Agnew, a geophysicist on the Scripps Institution of Oceanography on the University of California, San Diego. “It’s not a huge change in the Earth’s rotation that’s going to lead to some catastrophe or anything, but it is something notable. It’s yet another indication that we’re in a very unusual time.”
THE LENGTH OF EARTH’S DAY IS NOT SET IN STONE AND MAY SURPRISE YOU
Ice melting at each of Earth’s poles has been counteracting the planet’s burst of pace and is more likely to have delayed this international second of reckoning by about three years, Agnew stated.
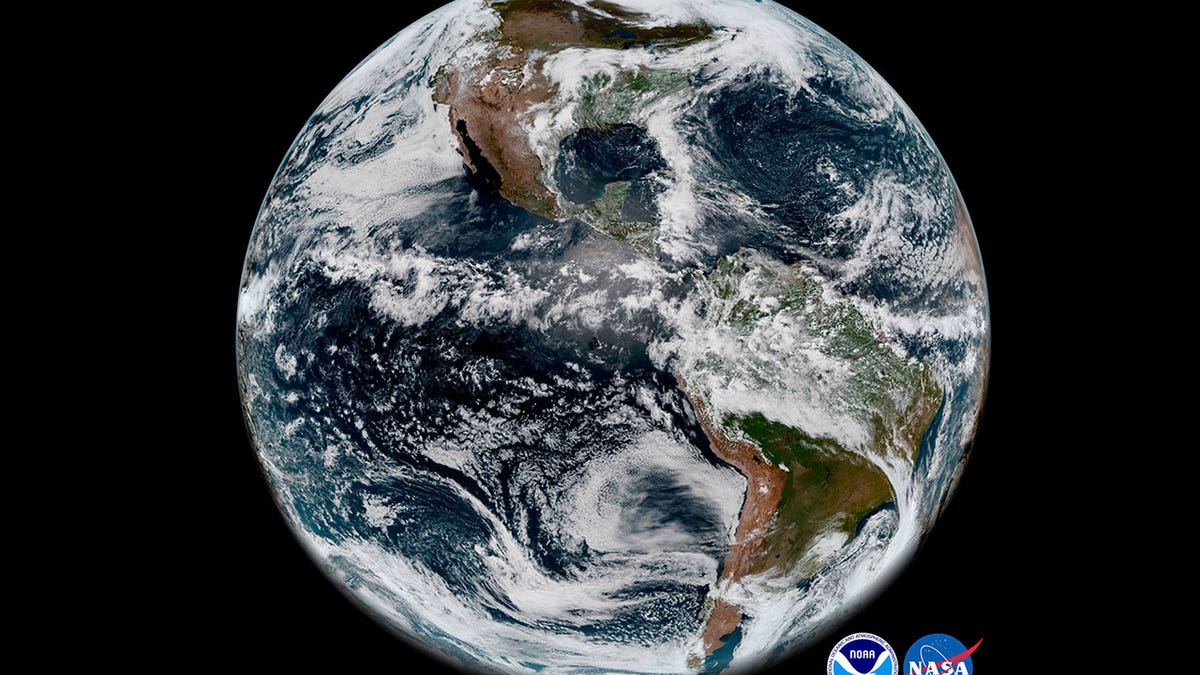
This satellite tv for pc picture reveals the Earth’s western hemisphere on May 20, 2018, made by the brand new GOES-17 satellite tv for pc. For the primary time in historical past, world timekeepers may have to think about subtracting a second from our clocks in a few years as a result of the planet is rotating sooner. (NOAA/NASA by way of AP, File)
“We are headed toward a negative leap second,” stated Dennis McCarthy, retired director of time for the U.S. Naval Observatory who wasn’t half of the research. “It’s a matter of when.”
It’s a difficult state of affairs that entails, physics, international energy politics, local weather change, expertise and two varieties of time.
Earth takes about 24 hours to rotate, however the important thing phrase is about.
SOLAR ECLIPSE 2024: WHERE AND HOW TO VIEW THE RARE ORBIT HITTING THE US
For 1000’s of years, the Earth has been typically slowing down, with the speed various from time to time, stated Agnew and Judah Levine, a physicist for the time and frequency division of the National Institute of Standards and Technology.
The slowing is generally brought on by the impact of tides, that are brought on by the pull of the moon, McCarthy stated.
This didn’t matter till atomic clocks have been adopted because the official time commonplace greater than 55 years in the past. Those didn’t gradual.
That established two variations of time — astronomical and atomic — they usually did not match. Astronomical time fell behind atomic time by 2.5 milliseconds on daily basis. That meant the atomic clock would say it’s midnight and to Earth it was midnight a fraction of a second later, Agnew stated.
Those every day fractions of seconds added as much as entire seconds each few years. Starting in 1972, worldwide timekeepers determined so as to add a “leap second” in June or December for astronomical time to catch as much as the atomic time, known as Coordinated Universal Time or UTC. Instead of 11:59 and 59 seconds turning to midnight, there can be one other second at 11:59 and 60 seconds. A detrimental leap second would go from 11:59 and 58 seconds on to midnight, skipping 11:59:59.
Between 1972 and 2016, 27 separate leap seconds have been added as Earth slowed. But the speed of slowing was petering out.
“In 2016 or 2017 or maybe 2018, the slowdown rate had slowed down to the point that the Earth was actually speeding up,” Levine stated.
Earth’s rushing up as a result of its scorching liquid core — “a large ball of molten fluid” — acts in unpredictable methods, with eddies and flows that adjust, Agnew stated.
Agnew stated the core has been triggering a speedup for about 50 years, however fast melting of ice on the poles since 1990 masked that impact. Melting ice shifts Earth’s mass from the poles to the bulging middle, which slows the rotation very similar to a spinning ice skater slows when extending their arms out to their sides, he stated.
Without the impact of melting ice, Earth would wish that detrimental leap second in 2026 as an alternative of 2029, Agnew calculated.
For a long time, astronomers had been preserving common and astronomical time along with these helpful little leap seconds. But pc system operators stated these additions aren’t straightforward for all of the exact expertise the world now depends on. In 2012, some pc programs mishandled the leap second, inflicting issues for Reddit, Linux, Qantas Airlines and others, specialists stated.
“What is the need for this adjustment in time when it causes so many problems?” McCarthy stated.
But Russia’s satellite tv for pc system depends on astronomical time, so eliminating leap seconds would cause them issues, Agnew and McCarthy stated. Astronomers and others needed to maintain the system that may add a leap second each time the distinction between atomic and astronomical time neared a second.
In 2022, the world’s timekeepers determined that beginning within the 2030s they’d change the requirements for inserting or deleting a leap second, making it a lot much less possible.
Tech firms akin to Google and Amazon unilaterally instituted their very own options to the leap second difficulty by steadily including fractions of a second over a full day, Levine stated.
“The fights are so serious because the stakes are so small,” Levine stated.
CLICK HERE TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP
Then add within the “weird” impact of subtracting, not including a leap second, Agnew stated. It’s more likely to be harder to skip a second as a result of software program applications are designed so as to add, not subtract time, McCarthy stated.
McCarthy stated the pattern towards needing a detrimental leap second is obvious, however he thinks it’s extra to do with the Earth changing into extra spherical from geologic shifts from the tip of the final ice age.
Three different outdoors scientists stated Agnew’s research is sensible, calling his proof compelling.
But Levine doesn’t suppose a detrimental leap second will actually be wanted. He stated the general slowing pattern from tides has been round for hundreds of years and continues, however the shorter traits in Earth’s core come and go.
“This is not a process where the past is a good prediction of the future,” Levine stated. “Anyone who makes a long-term prediction on the future is on very, very shaky ground.”
[ad_2]
Source hyperlink





