[ad_1]
An individual’s notion of time can both speed up or decelerate bodily healing, in response to a brand new study that factors to a powerful connection between the thoughts and physique on the subject of well being.
Researchers from Harvard University mentioned the findings problem typical medical knowledge in regards to the affect of psychological elements on bodily well being outcomes.
Decades of analysis into the psychological influences on bodily well being, such because the placebo impact – involving the administration of inert remedy – have led to important enhancements in remedies for a broad vary of diseases.
Approaches like mindfulness and cognitive behaviour remedy are additionally being thought of as remedy choices for circumstances of persistent ache.
The new study assessed how the impact of time on bodily healing is influenced by the psychological expertise of time.
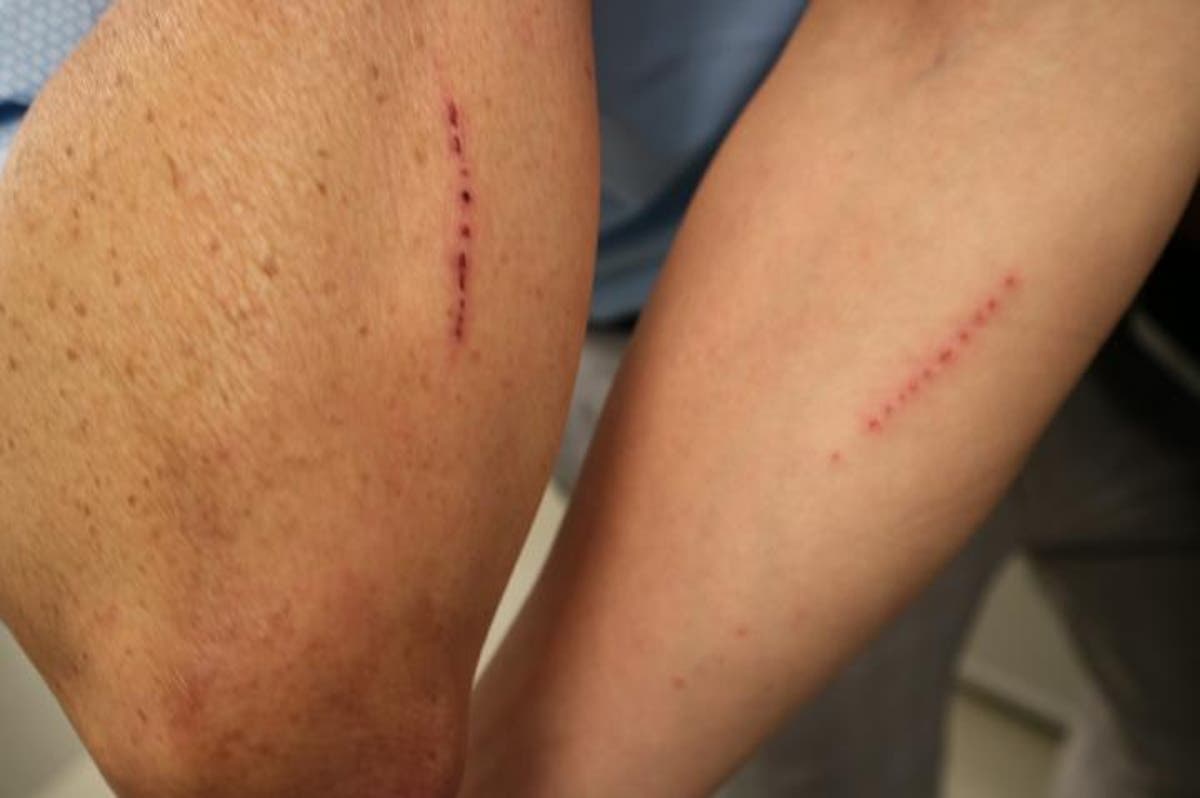
In the analysis, scientists from Harvard University used a standardised process to mildly bruise volunteer topics and manipulated their notion of time within the lab.
To trigger the injuries, individuals had been topic to cupping remedy, which entails making a localised suction on the pores and skin utilizing cups, which causes the enlargement of blood vessels beneath the pores and skin, resulting in bruising post-therapy.
Cupping was not used for any therapeutic function within the study, however slightly for the incidental marks left on the pores and skin after remedies.
A Mind and Body Breathing Technique could Reduce Alzheimer’s Risk
Each study participant then accomplished three experimental situations: gradual time (half of real-time); regular time, which was the identical as real-time; and quick time which was twice the speed of real-time.
Participants spent the identical quantity of real-time (28 min), however the perceived time in two of the situations was altered utilizing a manipulated timer such that the perceived time was equal to half for one set of topics (14 min) or double (56 min) the quantity of realtime for others.
Researchers noticed that wounds healed sooner in individuals who believed extra time had handed, and the healing course of appeared slower when a participant perceived much less time to have passed by.
“Compared to a control condition, in which perceived time and actual time were equal, we found that experimentally induced wounds healed faster when participants believed more time had passed, and slower when they believed less time had passed, even though the actual elapsed time was always the same,” scientists wrote.
“Our results demonstrate that the effect of time on physical healing is inseparable from the psychological experience of time,” they mentioned.
Until now, typical knowledge has held that psychological influences solely have an effect on well being not directly, primarily by influencing habits.
The newest findings, in response to researchers, make one more case of direct mind-body connection in human well being.
“Perceptions, expectations, beliefs, and so on are reflected throughout the mind–body and necessarily shape biological and physiological processes,” scientists added.
They mentioned extra analysis was wanted to grasp the underlying mechanisms and broader implications of those findings.
[ad_2]
Source hyperlink