[ad_1]
An historical species of great ape was probably pushed to extinction when local weather change put their favourite fruits out of attain throughout dry seasons, scientists reported Wednesday.
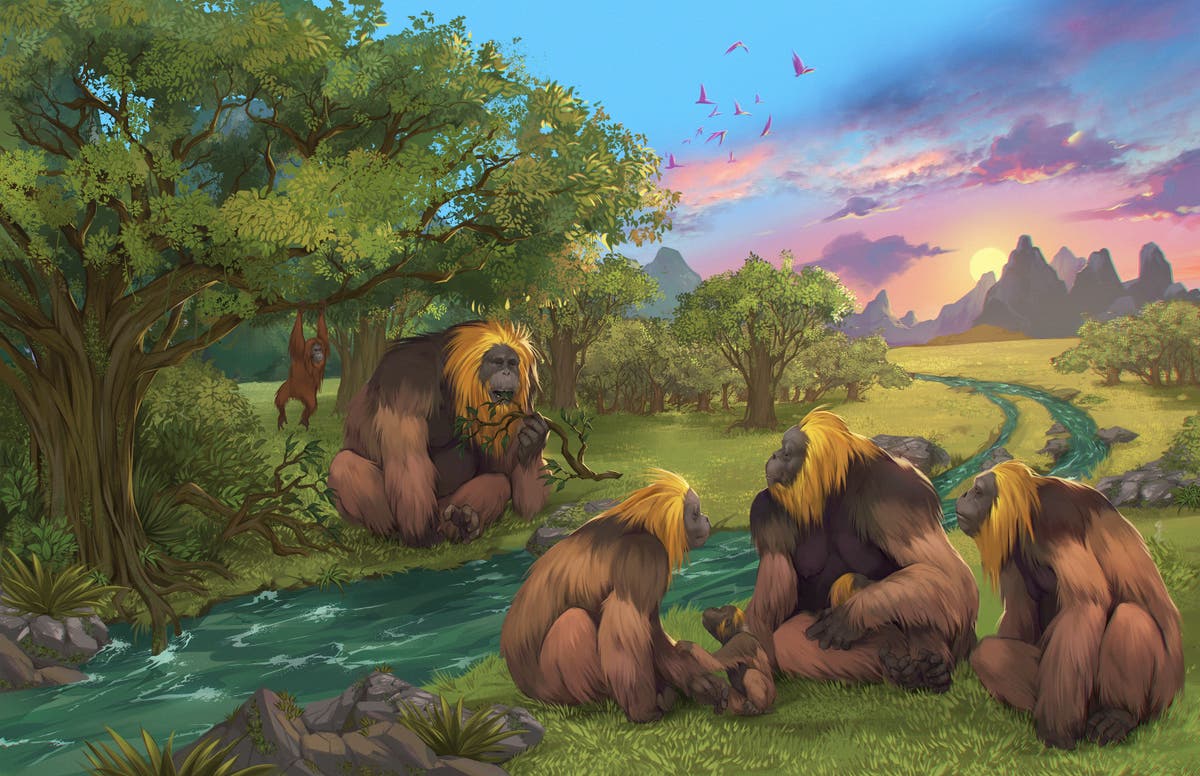
The species Gigantopithecus blacki, which as soon as lived in southern China, represents the largest great ape identified to scientists — standing 10 ft tall and weighing up to 650 kilos.
But its dimension may additionally have been a weak point.
“It’s just a massive animal – just really, really big,” stated Renaud Joannes-Boyau, a researcher at Australia‘s Southern Cross University and co-author of the research revealed in the journal Nature. “When food starts to be scarce, it’s so big it can’t climb trees to explore new food sources.”
(Yingqi Zhang, IVPP- CAS)
The big apes, which probably resembled trendy orangutans, survived for round 2 million years on the forested plains of China’s Guangxi area. They ate vegetarian diets, munching on fruits and flowers in tropical forests, till the setting started to change.
The researchers analyzed pollen and sediment samples preserved in Guangxi’s caves, in addition to fossil enamel, to unravel how forests produced fewer fruits beginning round 600,000 years in the past, as the area skilled extra dry seasons.
The big apes didn’t vanish rapidly, however probably went extinct someday between 215,000 and 295,000 years in the past, the researchers discovered.
While smaller apes could have been in a position to climb timber to seek for completely different meals, the researchers’ evaluation exhibits the big apes ate extra tree bark, reeds and different non-nutritious meals.
(Kira Westaway (Macquarie University)
“When the forest changed, there was not enough food preferred by the species,” stated co-author Zhang Yingqi of China’s Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology.
Most of what scientists learn about the extinct great apes comes from learning fossil enamel and 4 massive decrease jaw bones, all present in southern China. No full skeletons have been discovered.
Between round 2 and 22 million years in the past, a number of dozen species of great apes inhabited Africa, Europe and Asia, fossil data present. Today, solely gorillas, chimpanzees, bonobos, orangutans and people stay.
While the first people emerged in Africa, scientists don’t know on which continent the great ape household first arose, stated Rick Potts, who directs the Human Origins Program at the Smithsonian’s National Museum of Natural History and was not concerned in the research.
[ad_2]
Source hyperlink