[ad_1]
British youngsters are spending a lot time on social media that they’re shedding the flexibility to carry in-person conversations, one in all America’s most senior medical doctors has warned.
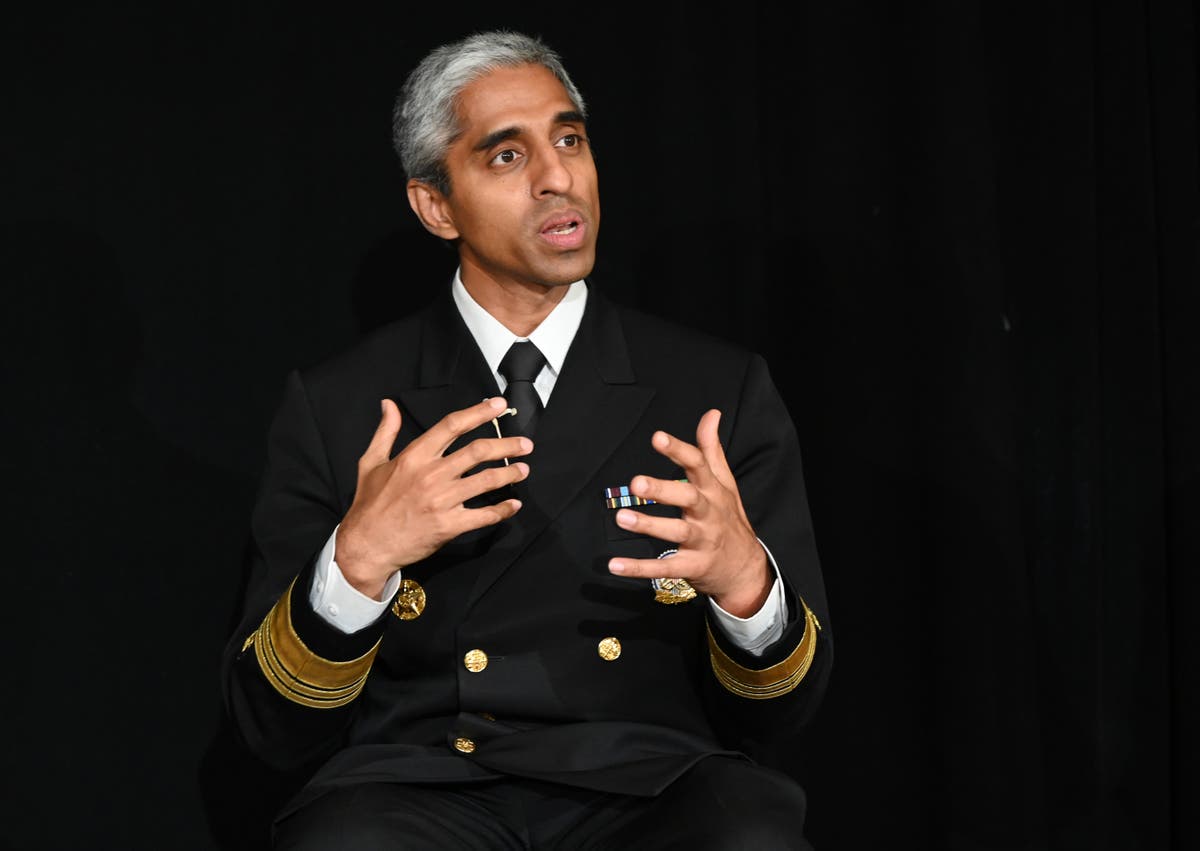
US surgeon-basic Vivek Murthy, who is on a analysis journey to the UK, stated younger individuals are more and more spending their lives on-line.
“That presents a real challenge because it became clear when talking to them, especially the university students, that their comfort with in-person interaction is diminishing over time, as we have less and less of it,” Dr Murthy advised The Times.
He additionally warned that individuals’s capacity to work together with each other typically and to construct relationships gave the impression to be diminishing.
Dr Murthy’s feedback got here following a report revealed in February which warned that the variety of younger individuals with poor psychological well being is rising within the UK.
The Resolution Foundation research discovered that one in three younger individuals aged 18 to 24 reported signs of psychological dysfunction, comparable to despair, anxiousness or bipolar dysfunction in 2021/22 – a considerably increased quantity than in 2000, when that determine stood at 24 per cent.
Dr Murthy has warned a number of occasions prior to now that extreme screen time is harming younger individuals.
Last yr, he issued a public well being advisory calling on US officers to deal with a “national youth mental health crisis” fuelled by extreme social media use.
“Children are exposed to harmful content on social media, ranging from violent and sexual content, to bullying and harassment. And for too many children, social media use is compromising their sleep and valuable in-person time with family and friends,” the surgeon-general warned on the time.
Combined with a scarcity of in-person social interplay, he says youngsters might not have individuals they will “confide in or talk to or be themselves with” contributing to extra loneliness.
Social networks supply a form of connection between individuals, he advised The Times, however can truly contribute to extra loneliness after they start changing in-person interactions.
“That’s just a fundamentally different quality of connection, which has a different level of impact on our happiness,” he stated.
[ad_2]
Source hyperlink