[ad_1]
- Scientists on Thursday described the fossilized cranium of a creature known as Kermitops gratus that lived in Texas about 270 million years in the past.
- The fossil was collected in 1984 close to Lake Kemp in Texas.
- It has been stored in the expansive assortment of the Smithsonian Institution’s National Museum of Natural History in Washington.
There undoubtedly have been no muppets throughout the Permian Period, however there was a Kermit – or at the least a forerunner of contemporary amphibians that has been named after the movie star frog.
Scientists on Thursday described the fossilized cranium of a creature known as Kermitops gratus that lived in what’s now Texas about 270 million years in the past. It belongs to a lineage believed to have given rise to the three dwelling branches of amphibians – frogs, salamanders and limbless caecilians.
While solely the cranium – measuring round 1.2 inches lengthy – was found, the researchers suppose Kermitops had a stoutly constructed salamander-like physique roughly 6-7 inches lengthy, although salamanders wouldn’t evolve for one more roughly 100 million years.
WHAT WE THOUGHT WE KNEW ABOUT T REX WAS WRONG, RESEARCHERS SAY IN NEW STUDY
Amphibians are considered one of the 4 teams of dwelling terrestrial vertebrates, together with reptiles, birds and mammals. The distinctive options of the Kermitops cranium – a mix of archaic and extra superior options – are offering perception into amphibian evolution.
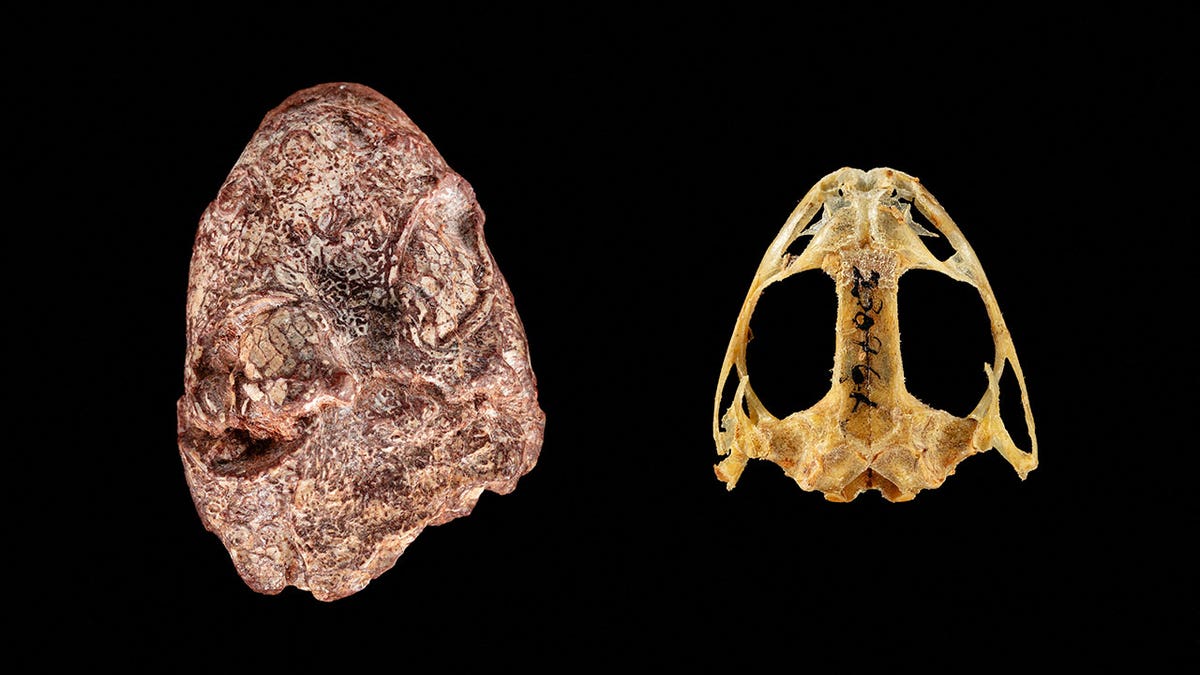
A composite picture is seen evaluating the fossil cranium of the Permian Period proto-amphibian Kermitops, left, with the cranium of a contemporary frog. (Brittany M. Hance, Smithsonian/Handout through REUTERS)
“Kermitops helps us understand the early history of amphibians by revealing there isn’t a clear trend of step by step becoming more like the modern amphibian,” mentioned Calvin So, a George Washington University paleontology doctoral scholar and lead writer of the research printed in the Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society.
The fossil was collected in 1984 close to Lake Kemp in Texas and stored in the expansive assortment of the Smithsonian Institution’s National Museum of Natural History in Washington, however was not completely studied till not too long ago.
Kermitops had a rounded snout, not not like frogs and salamanders. Preserved in its eye sockets have been palpebral bones – or eyelid bones – a function absent in immediately’s amphibians. Its cranium is constructed of roof-like bones, in distinction to the skinny and strut-like bones of contemporary amphibians.
“The length of the skull in front of the eyes is longer than the length of the skull behind the eyes, which differs from the other fossil amphibians living at the same time. We think this might have allowed Kermitops to snap its jaws closed faster, enabling capture of fast insect prey,” So mentioned.
The fossil file of early amphibians and their forerunners is spotty, making it tough to determine the origins of contemporary amphibians.
“Kermitops, with its unique anatomy, really exemplifies the importance of continuing to add new fossil data to understanding this evolutionary problem,” mentioned National Museum of Natural History paleontologist and research co-author Arjan Mann.
Kermit the Frog was created by the late American puppeteer Jim Henson in 1955, and a Kermit puppet made in the Nineteen Seventies is in the assortment of the Smithsonian’s National Museum of American History as an vital cultural object.
Kermitops means “Kermit face,” a nod to the muppet’s humorous look.
“We thought that the eyelid bones gave the fossil a bug-eyed look, and combined with a lopsided smile produced by slight crushing during the preservation of the fossil, we really thought it looked like Kermit the Frog,” So mentioned.
NORTH DAKOTA COAL MINERS UNEARTH ANCIENT MAMMOTH FOSSIL, INCLUDING 7-FOOT-LONG TUSK: ‘EXCITING FIND’
Kermitops belonged to a bunch known as temnospondyls that arose a couple of tens of thousands and thousands of years after the first land vertebrates developed from fish ancestors. The largest temnospondyls superficially resembled crocodiles, together with two that every have been round 20 ft in size, Prionosuchus and Mastodonsaurus.
Temnospondyls are thought of the progenitor lineage of contemporary amphibians, Mann mentioned.
Kermitops existed about 20 million years earlier than the worst mass extinction in Earth’s historical past and about 40 million years earlier than the first dinosaurs. It lived alongside different members of the amphibian lineage in addition to the spectacular sail-backed Dimetrodon, a predator associated to the mammalian lineage.
The surroundings wherein Kermitops lived seems to have alternated between heat and humid seasons and sizzling and arid seasons.
“This environment would be similar to modern-day monsoons that take place in the Southwest U.S. and Southeast Asia,” So mentioned.
[ad_2]
Source hyperlink





