[ad_1]
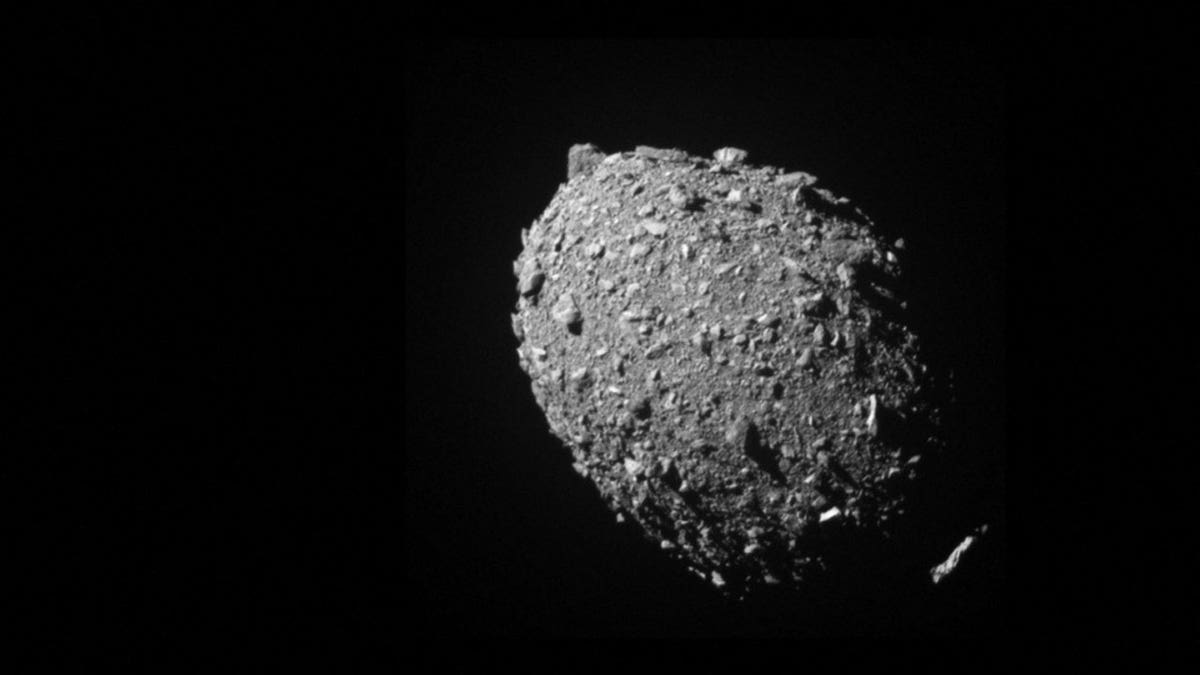
When NASA despatched its DART spacecraft to slam into the asteroid Dimorphos in 2022, the U.S. house company demonstrated that it was attainable to alter a celestial object’s trajectory, if wanted, to guard Earth. It seems that this collision changed not solely the asteroid’s path however its shape as properly.
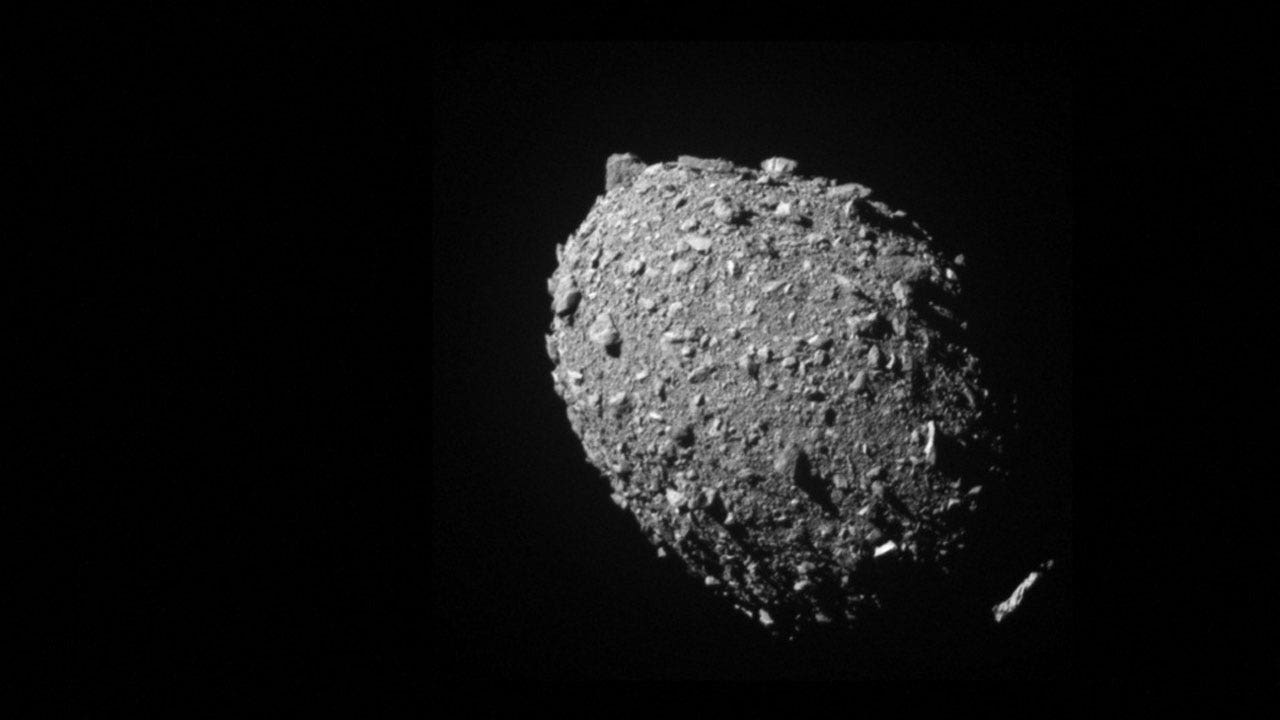
The asteroid, which earlier than the DART encounter appeared like a ball that was a bit plump within the waist, now seems to be formed extra like a watermelon – or, technically, a triaxial ellipsoid, scientists stated on Tuesday.
“The prevailing understanding is that Dimorphos is a loosely packed agglomeration of debris ranging from dust to gravel to boulders. Thus, its global strength is quite low, allowing deformation much more easily than for a solid monolithic body,” stated Steve Chesley, a senior analysis scientist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in California and a co-author of the examine revealed within the Planetary Science Journal.
NASA HEADQUARTERS RELEASES ITS BEST PHOTOS FROM 2023: SEE THE STUNNING PICTURES
“The shape change was so dramatic because of its rubble-pile composition,” stated JPL navigation engineer and examine lead creator Shantanu Naidu. “By measuring the pre- and post-impact orbit of Dimorphos, we were able to deduce the change in the shape of Dimorphos due to the DART impact.”
Dimorphos is a moonlet of Didymos, which is outlined as a near-Earth asteroid. The DART (Double Asteroid Redirection Test) mission was a proof-of-principle mission utilizing a spacecraft to use kinetic power to nudge a celestial object that in any other case could be on a collision course with Earth. Dimorphos and Didymos don’t pose an precise menace to Earth.
The spacecraft collided on Sept. 26, 2022, at about 14,000 miles per hour into Dimorphos, an asteroid that was about 560 ft extensive, roughly 6.8 million miles from Earth. Didymos has a diameter of a couple of half mile.

Asteroid moonlet Dimorphos is pictured right here as seen by the DART spacecraft 11 seconds earlier than influence on this picture taken by DART’s onboard DRACO imager. (NASA/Johns Hopkins APL/Handout through REUTERS)
DART’s collision, which despatched rocky particles from the asteroid flying into house, additionally changed the orbital path that Dimorphos takes round Didymos – making it elliptical as an alternative of round – and its orbital interval, the time it takes to finish a single orbit, the scientists stated. It now takes Dimorphos 11 hours, 22 minutes and 3 seconds to finish an orbit, 33 minutes and 15 seconds lower than earlier than the influence, they discovered.
Scientists had beforehand disclosed that the asteroid’s orbit had changed, with the brand new examine providing probably the most exact readings but on that.
Chesley stated the asteroid’s orbital interval continued to decay slowly within the weeks after the influence.
“We believe that this is due to the fact that loose debris in the system continues to leak out and carries angular momentum with it, thus necessarily contracting the orbit,” Chesley added. Angular momentum refers to how a lot a rotating object’s mass is distributed round its axis and how rapidly it’s spinning.
Dimorphos’ common orbital distance from Didymos is now about 3,780 ft, roughly 120 ft lower than earlier than the influence, the examine discovered.
CLICK HERE TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP
The researchers based mostly their conclusions on the shape and orbit of Dimorphos on observations from ground-based telescopes of how daylight reflecting off the surfaces of the 2 asteroids changed over time, information from radio waves bouncing off the asteroids and pictures DART obtained throughout its rendezvous.
More data is anticipated within the close to future in regards to the two asteroids. The European Space Agency’s Hera spacecraft is because of launch in October and attain them in late 2026 to verify issues out.
“We are anxiously awaiting the arrival of ESA’s Hera spacecraft, when we will be able to compare our modeled shape with that obtained from Hera imagery. We will also learn how much the orbit has changed since we last observed it in 2023,” Chesley stated.
[ad_2]
Source hyperlink