[ad_1]
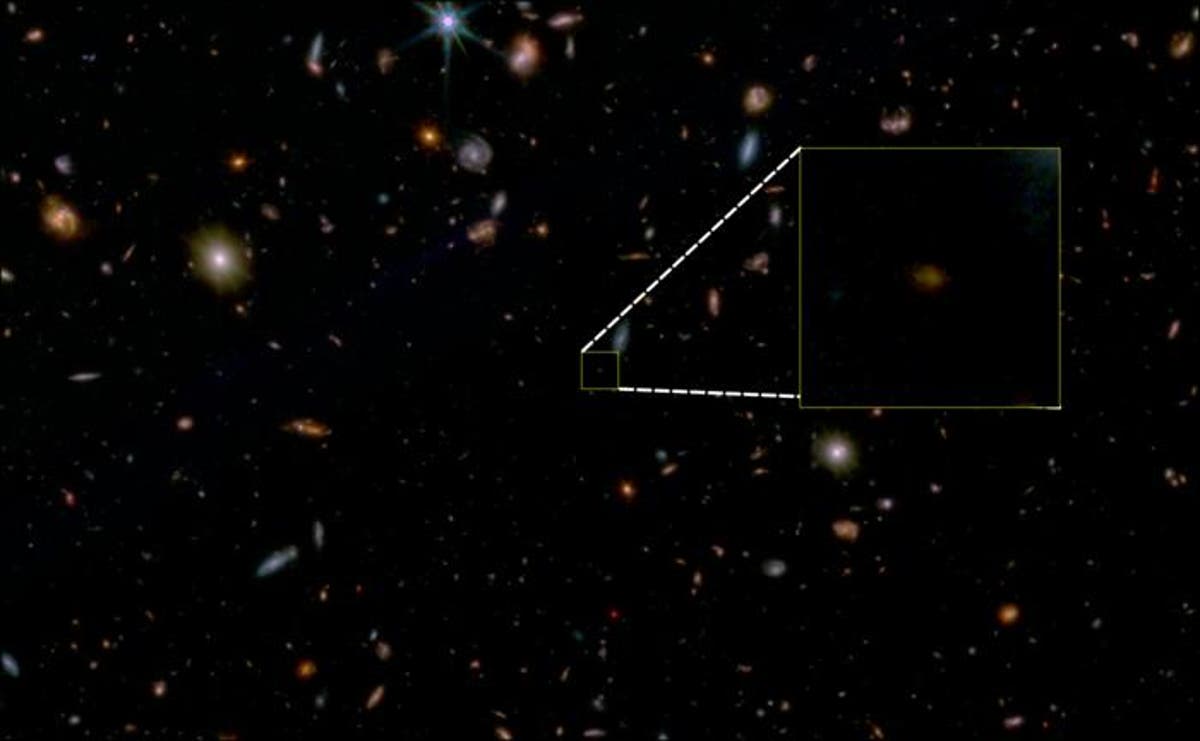
Scientists have found a “dead” galaxy older than any but found.
The new cluster of stars was already dead when the universe was at its starting. It seems to have burnt out when the cosmos was simply 5 per cent of its present age.
Star formation had already stopped within the galaxy some 13.1 billion years in the past, simply 700 million years after the universe started. While scientists have found comparable “dead” galaxies earlier than, it’s the oldest by 500 million years.
Scientists say the galaxy lived quick and died younger, the Cambridge researchers who found it stated. Such behaviour was not anticipated till the brand new galaxy was found.
“The galaxy seemed to have lived fast and intensely, and then stopped forming stars very rapidly,” stated astrophysicist Tobias Looser of the Kavli Institute for Cosmology on the University of Cambridge, lead writer of the research printed within the journal Nature.
“In the first few hundred million years of its history, the universe was violent and active, with plenty of gas around to fuel star formation in galaxies. That makes this discovery particularly puzzling and interesting,” Looser added.
This galaxy is comparatively small, with maybe 100 million to at least one billion stars. That would put it within the neighborhood of the mass of the Small Magellanic Cloud dwarf galaxy located close to our Milky Way, although that one continues to be forming new stars.
After a galaxy stops forming new stars, it turns into a bit like a stellar graveyard.
“Once star formation ends, existing stars die and are not replaced. This happens in a hierarchical fashion, by order of stellar weight, because the most massive stars are the hottest and shine the brightest, and as a result have the shortest lives,” Kavli Institute astrophysicist and research co-author Francesco D’Eugenio stated.
“As the hottest stars die, the galaxy color changes from blue – the color of hot stars – to yellow to red – the color of the least massive stars,” D’Eugenio added. “Stars about the mass of the sun live about 10 billion years. If this galaxy stopped forming stars at the time we observed it, there would be no sun-like stars left in it today. However, stars much less massive than the sun can live for trillions of years, so they would continue to shine long after star formation stopped.”
The researchers decided that this galaxy skilled a burst of star formation spanning 30 to 90 million years, then it all of a sudden stopped. They try to determine why.
It might be, they stated, as a result of motion of a supermassive black gap on the galactic middle or a phenomenon known as “feedback” – blasts of power from newly fashioned stars – that pushed the fuel wanted to type new stars out of the galaxy.
“Alternatively, gas can be consumed very quickly by star formation, without being promptly replenished by fresh gas from the surroundings of the galaxy, resulting in galaxystarvation,” Looser stated.
NASA’s Webb is ready to take a look at larger distances, and thus farther again in time, than its Hubble Space Telescope predecessor. Among different discoveries, Webb has enabled astronomers to see the earliest-known galaxies, which have turned out to be bigger and extra plentiful than anticipated.
In the brand new research, the researchers have been in a position to observe the dead galaxy at one second in time. It is feasible, they stated, that it later resumed star formation.
“Some galaxies may undergo rejuvenation, if they can find fresh gas to convert into new stars,” D’Eugenio stated. “We do not know the ultimate fate of this galaxy. This may depend on what mechanism caused star formation to stop.”
Additional reporting by Reuters
[ad_2]
Source hyperlink