[ad_1]
Researchers might have discovered a new means to goal the sources of sure brain issues.
In a research led by scientists at Mass General Brigham, deep brain stimulation (DBS) was ready to pinpoint dysfunctions within the brain which are answerable for four cognitive issues: Parkinson’s illness, dystonia (a muscle dysfunction situation that causes repetitive or twisting actions), obsessive compulsive dysfunction (OCD) and Tourette’s syndrome.
The discovery, printed in Nature Neuroscience on Feb. 22, could probably assist docs decide new treatments for these issues.
BOOST BRAIN HEALTH AND SLOW MENTAL AGING WITH 10 INTRIGUING TIPS FROM LONGEVITY EXPERTS
The research included 261 sufferers worldwide — 70 had dystonia, 127 have been Parkinson’s illness sufferers, 50 had been recognized with OCD and 14 had Tourette’s syndrome.
The researchers implanted electrodes into the brains of every participant and used particular software program to decide which brain circuits have been dysfunctional in every of the four issues.
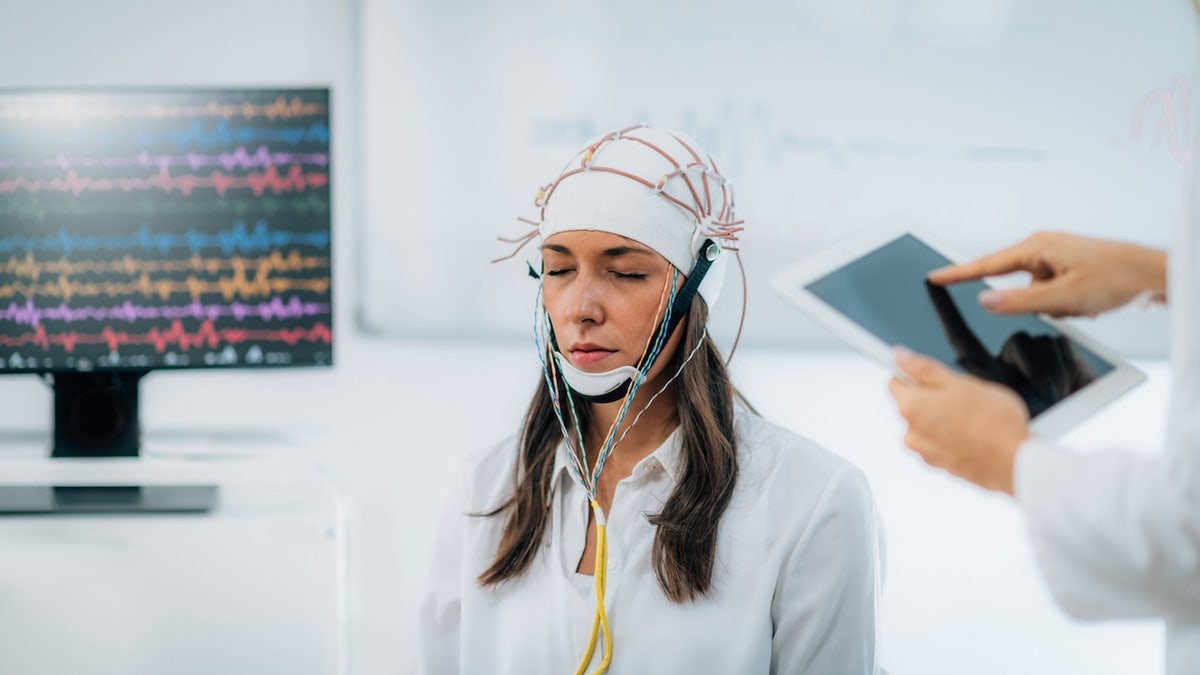

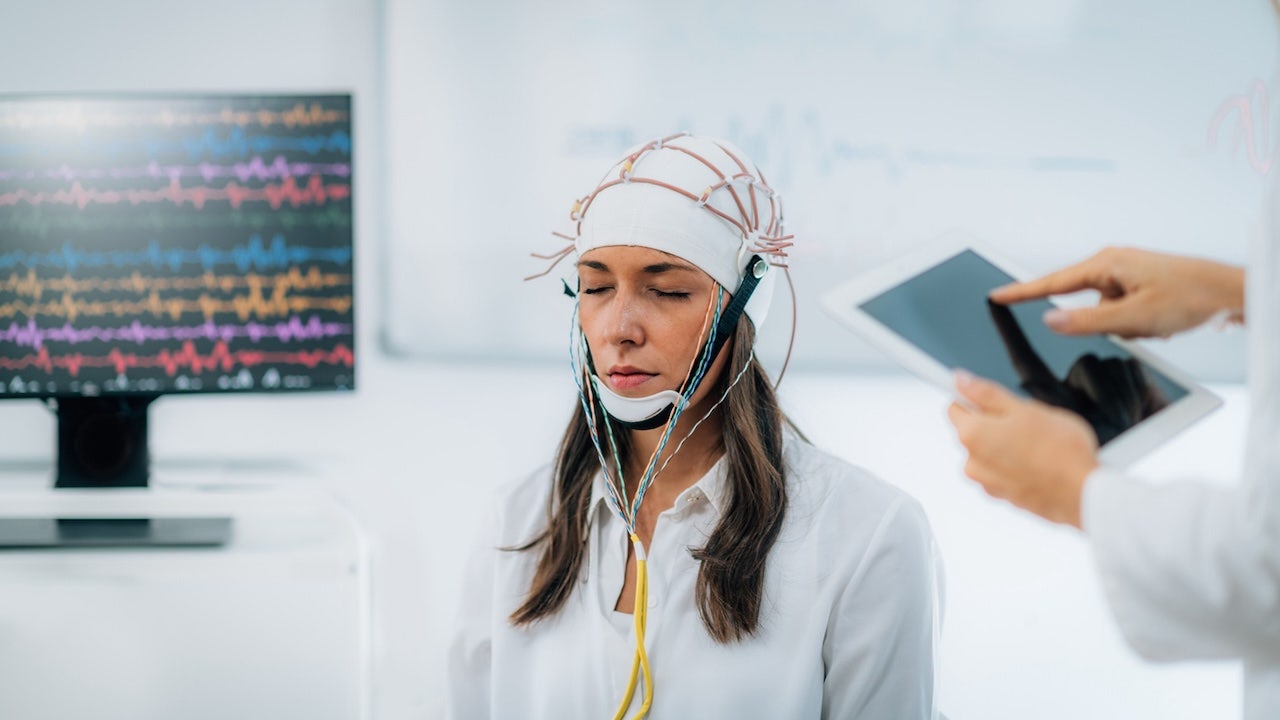
Deep brain stimulation has been used to pinpoint dysfunctions within the brain which are answerable for four cognitive issues. (iStock)
“In simplified terms, when brain circuits become dysfunctional, they may act as brakes for the specific brain functions that the circuit usually carries out,” Andreas Horn, M.D., PhD, affiliate professor of neurology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, mentioned in a press launch.
“Applying DBS may release the brake and may in part restore functionality.”
WORST FOODS AND DRINKS FOR BRAIN HEALTH, ACCORDING TO NUTRITION EXPERTS
Horn, one of the 39 researchers from 16 establishments who co-authored the research, went into extra element in a dialog with Fox News Digital.
“Based on the present findings, we can better understand why deep stimulation to a small subcortical structure in the brain has been helping patients with various disorders,” he mentioned.
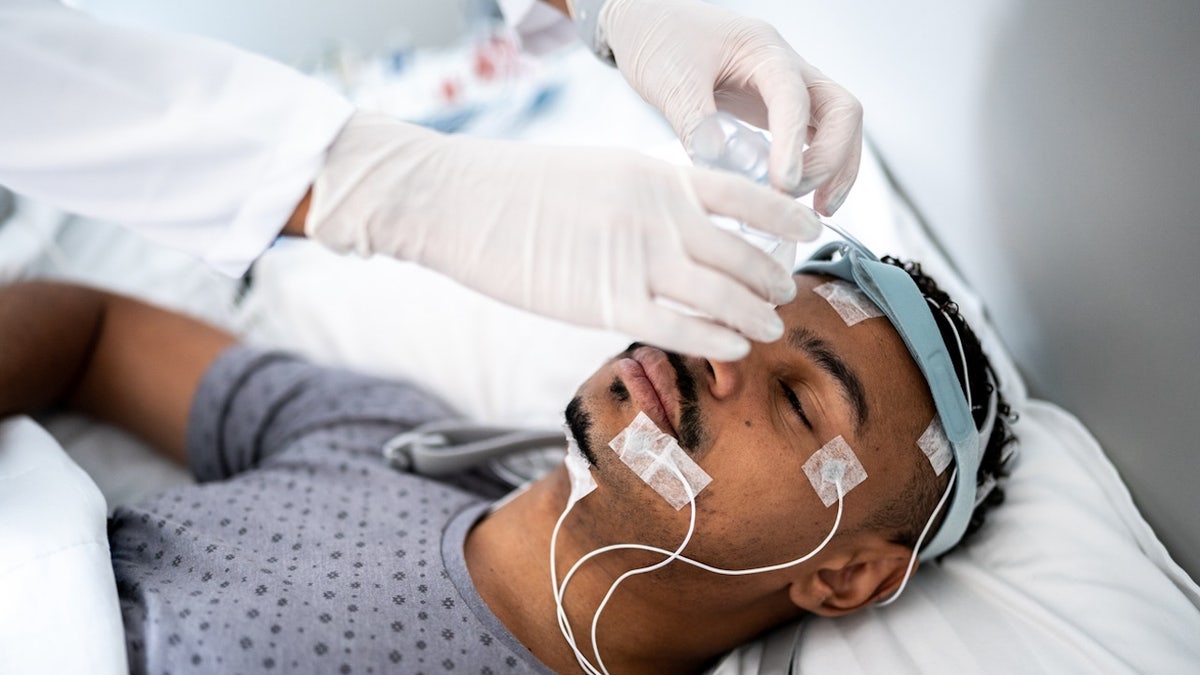
The researchers implanted electrodes into the brains of every participant (not pictured) and used particular software program to decide which brain circuits have been dysfunctional in every of the four issues. (iStock)
For every of the issues, a distinct brain community was recognized as “dysfunctional,” main to the situation, the physician mentioned.
“Identifying these ‘malfunctioning networks’ may help us better understand the four disorders and better target neuromodulation to help patients by alleviating symptoms,” he famous.
In three circumstances, the researchers discovered that making use of DBS led to “preliminary improved results.”
At Massachusetts General Hospital, one feminine affected person in her early 20s was recognized with extreme, treatment-resistant OCD.
After receiving electrode implantation and focused stimulation, the researchers measured a “significant improvement” in her signs one month after remedy, in accordance to the discharge.

Obsessive-compulsive dysfunction was one of the cognitive circumstances focused within the new research. (iStock)
Dr. Shannon Dean, a pediatric neurologist with the Kennedy Krieger Institute in Maryland, was not concerned within the research however shared her response to the findings.
“This study is an elegant demonstration of how treatment-focused and basic mechanism-based research can help guide each other,” she advised Fox News Digital.
“The authors used deep brain stimulation electrodes, which is an invasive surgical treatment for a variety of neurological disorders when medications alone are not enough,” Dean went on.
“I was interested to see the researchers then used their findings to refine exactly how they were treating several patients — and saw their patients’ symptoms improve as a result,” she mentioned.
Given the small quantity of contributors, Dean burdened the necessity for warning in deciphering the outcomes.
“What the authors found for those disorders will need to be replicated for us to be sure the conclusions are right,” she mentioned.
“However, what they have found is exciting and makes sense based on what we already know about these disorders. This points us to where future studies should be looking.”
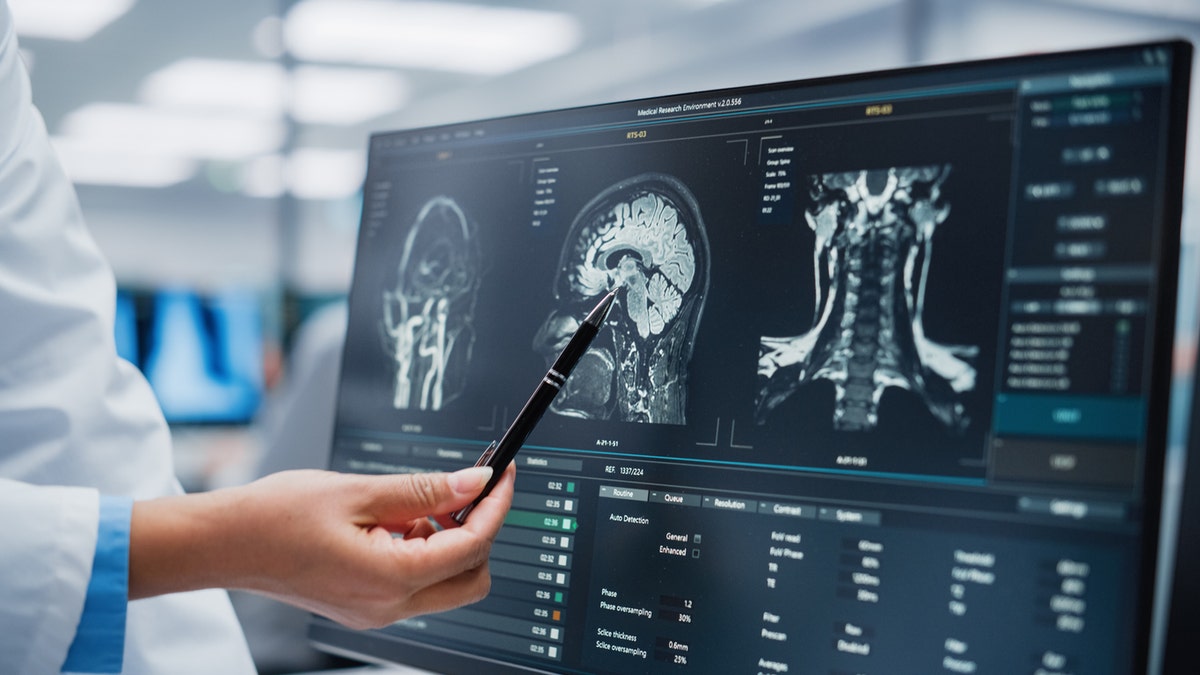
For every of the issues, a distinct brain community was recognized as “dysfunctional,” main to the situation, a researcher mentioned. (iStock)
“This research provides hope for people living with these diseases who are resistant to standard medical therapy,” she added.
Dr. Arif Dalvi, a neurologist on workers at St. Mary’s Medical Center in Florida, additionally commented on the research as an out of doors knowledgeable.
“Even though deep brain stimulation has been part of the standard of care for neurological conditions such as Parkinson’s disease and tremors for decades, the technology continues to evolve,” he advised Fox News Digital.
“This research provides hope for people living with these diseases who are resistant to standard medical therapy.”
“This analysis identified ‘sweet spots’ within these circuits that could significantly alleviate symptoms, demonstrating the efficacy of DBS in modulating neural activity.”
The findings spotlight the necessity for customized therapies, Dalvi famous.
“This emphasizes a need for neurologists to carefully evaluate each patient as a unique individual and tailor a specific treatment plan, rather than working off generic best practices or therapeutic guidelines,” he mentioned.
Study was restricted, researchers say
This analysis is seen as step one in what shall be an extended course of, Horn mentioned.
“The study is based on retrospective data — main results should be confirmed by prospective trials, which represent the gold standard to accumulate evidence in science and medicine,” he advised Fox News Digital.

Developing extra refined mapping strategies and understanding the long-term results of deep brain stimulation shall be essential, a neurologist mentioned. (iStock)
The research’s pattern dimension was additionally comparatively small, he mentioned, particularly for Tourette’s.
“Even globally, not many patients have undergone deep brain stimulation surgery for this disorder,” Horn mentioned.
This research is step one in defining what the researchers name the “human dysfunctome,” the set of connections which will develop into dysfunctional in particular neurological or psychiatric issues of the human brain.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
“We first paint a picture of the dysfunctome, but need additional data to complete the picture and map other symptoms onto the circuits of the human brain,” Horn mentioned.
While the research findings won’t lead to drastic adjustments simply but, Horn mentioned they might assist skilled clinicians fine-tune their approaches to neurology treatments.

The findings from this research level within the course of extra customized cognitive therapies, consultants mentioned. (iStock)
“It could give additional clarity or small refinements here and there to make interventions more successful,” Horn mentioned. “However, the information should not be followed blindly, but instead should be validated in prospective studies.”
The researchers are already beginning to plan for medical trials to validate the outcomes.
CLICK HERE TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP
As Dalvi identified, creating extra refined mapping strategies and understanding the long-term results of deep brain stimulation shall be essential.
“Additionally, expanding this approach to other brain regions and disorders could uncover new therapeutic avenues, marking a new era in the treatment of neurological conditions,” he added.
For extra Health articles, go to www.foxnews.com/well being.
[ad_2]
Source hyperlink





